A new research on reshaping how scientists understand the first days of the formation of the Earth – where it acquires that the deep interior of our planet is closed in its specific features Only 100 million years After her birth. Leave the physicist at York University Charles-Diuruard Boukarithe study –Posted in nature_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The results challenge the long assumptions in the science of planets and make a rare glimpse How to develop rocky planetsBoth in our solar system and beyond.
A young planet with chaotic interior design
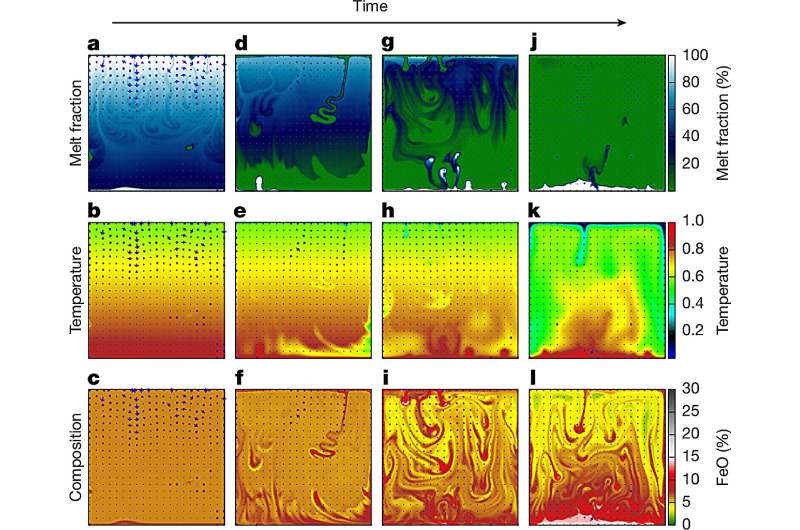
In its first stage, the earth was Magma– turbulent mass, partially photographed from silicate wrapped around the molten heart. As the planet cools, the interior design began to consolidate. Until now, most of the models have slowly supposed to sclerosis, under severe pressure, and dictate a chemistry Lower cloakThe huge layer located above the heart of the earth.
But the Boukari team has developed a New material model Simulating how molten rock crystals were formed as the scarf is. Their simulations revealed a surprise: Most of the crystals that were formed in low pressure near the surface, instead of the deep ground. This indicates Chemical makeup The bottom scarf of the Earth was affected by dynamics at the surface level during the first planet period.
“Until now, we assumed that geological chemistry in the bottom scarf may probably be controlled by high pressure chemical reactions,” Boukari explains. “Now it seems that we also need to calculate their counterparts in low pressure.”
A planetary personality is formed in her youth
Using a Pciential flow approachThe researchers simulated how different materials acted in the molten earth cloak under the circumstances of the planets. Since the chilled solid molecules are formed, drowning or floating based on their density – which greatly creates distinctive layers with chemical fingerprints.
The study attracts an analogy between the formation of planets and human development: “If you take children, they sometimes do crazy things because they have a lot of energy, such as planets when they are young,” Boukari noted. “There are some aspects of the early development of the planets that we can already see in their structure today.”
In this case, the earth Lower cloakWhich affects the heat flow, the generation of the magnetic field, and the plate’s lake-it is likely to be formed through high-energy chaos in the first 100 million years.
Classes older than Earth?
Some crystal patterns that have been studied in the form may reflect the existing conditions Before forming the entire landWhen the materials of the solar nebula are still Trex. This makes these chemical signatures among the oldest geological features on this planet – probably preceding the end of the Earth.
These results are not only reshaping the timetable for the geological development of the Earth, but also suggests this Other rocky planets It may maintain evidence about their early history in ways we have just started understanding.
A new tool to predict other worlds
Because the model connects Early thermal and chemical conditions To the structure of the current planets, they can be used to predict how to develop other planets-including external planets.
Boukari said: “If we know a kind of starting circumstances, and we know the main processes of the development of planets, we can predict how the planets develop.” This insight is crucial to understanding The susceptibility of educationInternal dynamics and magnetic field generation – the elements of the key to preserving life.
While planetarians continue to compare the Earth with other rock bodies such as Mars, MercuryAnd VenusThis study provides a new framework for deciphering what lies below the surface – by looking away to the years of the planet’s training.









